As Australia resets to a more ambitious 2030 emissions target under a new Labor government, it’s time we address the largest opportunity on our pathway to net zero emissions: “making dirty cleaner”. David Gilmour, Portfolio Analyst and ESG Specialist, details why.
As Australia resets to a more ambitious 2030 emissions target under a new Labor government, it’s time we address the largest opportunity on our pathway to net zero emissions: “making dirty cleaner”.
For too long, sustainability investment has centred on future facing industries, like renewables, and blatantly ignored the dirtiest industries. The focus has been on the cure to emissions, with no consideration to prevention. Divestment has been the weapon of choice.
The Ukraine-Russia war has been a wake-up call. Fossil fuels, despite Western efforts to curb supply, are necessary for energy security when global trade is dividing into geopolitical blocks. What’s more, they continue to dominate the world’s growing demand for energy (Chart 1). To break their nexus with economic growth – and simultaneously transition without widening wealth inequality – we need to solve the demand side for both industry and the consumer. And that requires investor support and engagement.
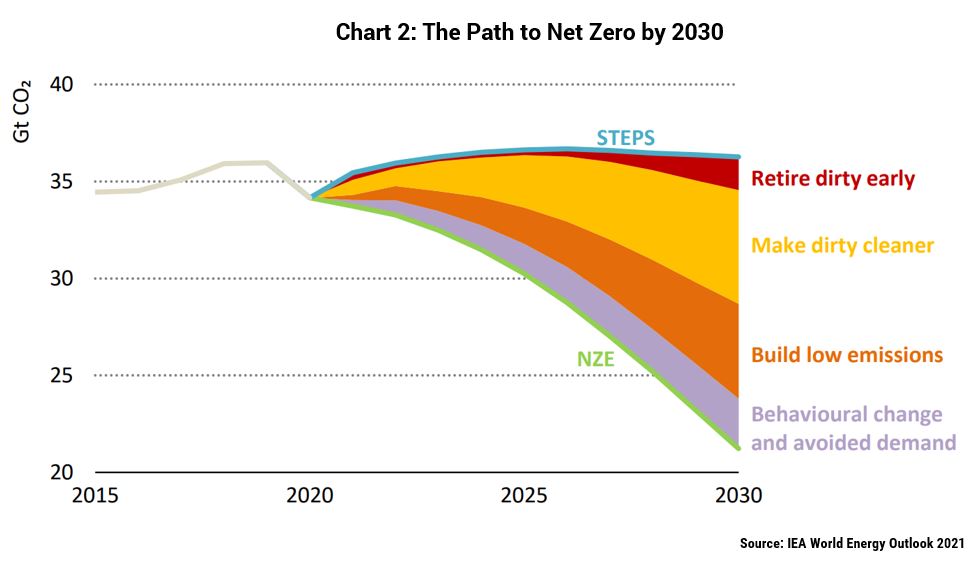
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), we cannot simply divide energy investments into “clean” and “dirty”. In fact, the largest part of emissions reductions under its net zero scenario – the same one purists cite when arguing to cease new fossil fuel production – comes from a middle ground of “transition” investments (Chart 2). Examples include project enhancements to reduce methane leakage, efficiency or flexibility measures in industrial processes, coal-to-gas switching (e.g. new gas boilers), refurbishments of power plants to support co-firing with low emissions fuels, and gas-fired plants that enable higher renewables penetration.
Within Goldman Sachs’ latest forecast for a 37% fall in US emissions by 2030[1] (below the Biden Administration’s target 50-52% reduction), energy efficiency is the first of three themes driving emissions lower over the short term. Outside Utilities, GS forecasts the biggest reductions to come from Oil & Gas Producers, Diversified Metals & Mining and Aluminium[2] – sectors where ownership by ESG focused investors is limited.
Domestically it’s a similar story. Like the US, Australia’s electricity sector only accounts for around 30% of total emissions. Labor’s new target for a 43% reduction on emissions to 2030 (based on 2005 levels) will require substantive efforts from Industry and Transport since, as we discussed last year, the Electricity sector is already stretched to its limit with a forecast 49% reduction by 2030 from today’s levels.
When you dig into the numbers, Labor’s target equates to -30% on 2020 emissions levels, from 512MT today to 356Mt in 2030. This compares to the Coalition’s projection for 439MT by 2030 (-14%) (Table 1). If we assume no further emissions reductions in the electricity sector under Labor, then it needs a -22% reduction in emissions from the “Other” sources, versus the Coalition’s former forecast for +1%.
The new Federal government has also committed to strengthening the existing Safeguard Mechanism (SGM) to support its national target. Currently, Australia’s largest emitting facilities (>100,000 tonnes per annum) have to purchase credits (ACCUs) when their emissions rise above generously set baselines. We support Labor’s proposal to reduce these baselines over time which, if enacted, will drive greater energy efficiency and lowest-cost abatement solutions.
Investors must also play an important role. We believe strongly in company engagement over exclusion; the former can lead to outperformance, while the latter shifts ownership to parts of the market with less oversight and deprives companies of capital when they need it most. That’s why we are shareholders in high emitters such as Alumina (AWC), a company with a harder pathway to net zero but has the capability to benefit from the transition. AWC is already among the lowest emitters among major alumina producers, is pursuing early-stage technologies and is a clear beneficiary of green capex given the expected growth in demand for aluminium (39% demand growth to 2030[3]). We are also overweight Worley (WOR), which is well positioned to capture higher structural demand from energy transition work over and above its traditional work for the oil & gas industry.
Once we solve the demand side, we expect supply from the oil & gas industry will take care of itself as customers evaporate. Until then Australian gas producers enjoy a privileged position. They are low sovereign risk for European countries weaning themselves off Russian gas, and will contribute significantly to lowering emissions in Asia as coal-to-gas switching takes place. Early this year we established a position in Woodside Petroleum (WPL), a company which predominantly produces gas and has a new strategy to invest $US5bn in new energy opportunities by 2030. Our focus remains on working with management to strengthen its 2030 interim target and lower its reliance on offsets.
As ever, we continue to test the resolve of Australian companies to reduce their exposure to climate change risks and whether they are pursuing the right opportunities in the transition. Importantly, we have no intention of sidelining companies that provide critical products, especially when cleaning up their operations will cause the largest reductions in global emissions to a low carbon future.


0 Comments